At the ‘Made by Google’ event, Google launched Pixel 3 sharing its newly introduced camera features, and one of them was Top Shot. Last week, it shared further details on how Top Shot works. Top Shot saves and analyzes the image taken before and after the shutter press on the device in real-time using computer vision techniques and then recommends several alternative high-quality HDR+ photos.
How Top Shot works?
Once the shutter button is pressed, Top Shot captures up to 90 images from 1.5 seconds before and after the shutter press, and simultaneously selects up to two alternative shots to save in high resolution. These alternative shots are then processed by Visual Core as HDR+ images with a very small amount of extra latency and are embedded into the file of the Motion Photo.
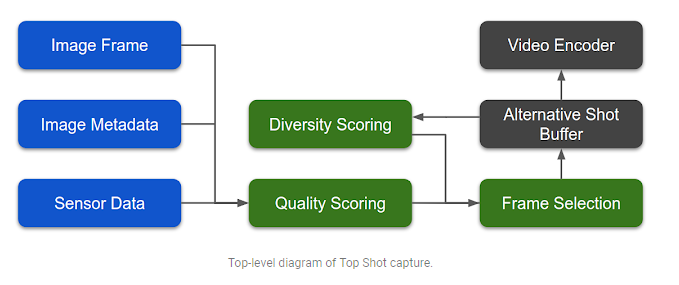
Top Shot analyzes captured images based on three attributes: functional qualities like lighting, objective attributes like whether the people in the image are smiling, and subjective qualities like emotional expressions. It does this by using a computer vision model, an optimized version of the MobileNet model, which operates in low latency, on-device mode.
In early layers, the model detects low-level visual attributes like it identifies whether the subject is blurry. In subsequent layers, it detects more complex objective attributes like whether the subject’s eyes are open and subjective attributes like whether there is an emotional expression of amusement or surprise.
The model was trained using a technique named knowledge distillation, which compresses the knowledge in an ensemble of models into a single model, over a large number of diverse face images using quantization during both training and inference. To predict the quality scores for faces, Top Shot uses a layered Generalized Additive Model (GAM) and combines them into a weighted-average “frame faces” score.
For the use cases where faces are not the primary subject, three more scores are added to the overall frame quality scores. These scores are subject motion saliency score, global motion blur score, and 3A scores (auto exposure, autofocus, and auto white balance). All these scores were used to train the model predicting an overall quality score, which matches the frame preference of human raters, to maximize end-to-end product quality.
To read more in detail, check out the post on the Google AI Blog.
Read Next
Google launches new products, the Pixel 3 and Pixel 3 XL, Pixel Slate, and Google Home Hub
Google’s Pixel camera app introduces Night Sight to help click clear pictures with HDR+
Google open sources DeepLab-v3+: A model for Semantic Image Segmentation using TensorFlow










![How to create sales analysis app in Qlik Sense using DAR method [Tutorial] Financial and Technical Data Analysis Graph Showing Search Findings](https://hub.packtpub.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/iStock-877278574-218x150.jpg)